Stellio: Difference between revisions
IanRidpath (talk | contribs) (→IAU Working Group Star Names: Added info on brightest stars) |
IanRidpath (talk | contribs) (→IAU Working Group Star Names: Cap A for Alpha) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Latin "Stellio", literally "star lizard", derives from "stella" (star). It designates a [https://www.britannica.com/animal/newt newt], an olive-green lizard with spotted back, typically found in the rocky areas around the Mediterranean. It is also known as "stellion" or "rock agama"; scientific name is ''Laudakia stellio'' of the family of the ''Agamidae''. |
Latin "Stellio", literally "star lizard", derives from "stella" (star). It designates a [https://www.britannica.com/animal/newt newt], an olive-green lizard with spotted back, typically found in the rocky areas around the Mediterranean. It is also known as "stellion" or "rock agama"; scientific name is ''Laudakia stellio'' of the family of the ''Agamidae''. |
||
In [https://www.e-rara.ch/zut/content/zoom/133606 the introduction of their atlas], Jan and Elizabeta Hevelius claim that they have named this region after a lizard because the lizard is squeezed into such a narrow gap between existing constellations that no larger animal could fit there.<ref>Ian Ridpath ([http://www.ianridpath.com/startales/lacertahevelius.html# Website], 2024). Hevelius on the constellation "Lacerta or Stellio". </ref> |
In [https://www.e-rara.ch/zut/content/zoom/133606 the introduction of their atlas], Jan and Elizabeta Hevelius claim that they have named this region after a lizard because the lizard is squeezed into such a narrow gap between existing constellations that no larger animal could fit there.<ref>Ian Ridpath ([http://www.ianridpath.com/startales/lacertahevelius.html# Website], 2024). Hevelius on the constellation "Lacerta or Stellio". </ref> |
||
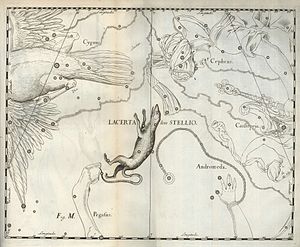
| ⚫ | On Hevelius’s chart (right) there is a triangle of stars above the head of Lacerta that are shown as part of the turban of Cepheus. These stars are now included in Lacerta, and are known as Alpha Lacertae (mag. 3.8), Beta Lacertae (4.4), and 9 Lacertae (4.6). The Greek letters were allocated by Francis Baily in his ''British Association Catalogue'' of 1845. |
||
==Mythology== |
==Mythology== |
||
| Line 13: | Line 15: | ||
==IAU Working Group Star Names== |
==IAU Working Group Star Names== |
||
Following the Almagest-tradition of using alternative names for the constellation given by its creator to the brightest star in the group, the name "Stellio" was suggested for the brightest star in [[Lacerta]], α Lac (Alpha Lacertae). It was discussed and approved by the IAU WGSN in 2024. |
|||
| ⚫ | On Hevelius’s chart (right) there is a triangle of stars above the head of Lacerta that are shown as part of the turban of Cepheus. These stars are now included in Lacerta, and are known as Alpha Lacertae (mag. 3.8), Beta Lacertae (4.4), and 9 Lacertae (4.6). The Greek letters were allocated by Francis Baily in his ''British Association Catalogue'' of 1845. |
||
The name "Stellio" is suggested for the brightest os these stars, Alpha Lacertae. |
|||
On August 29th 2024, the IAU WGSN decided to adopt the name "Stellio" for [https://simbad.cds.unistra.fr/simbad/sim-id?Ident=alf+Lac&NbIdent=1&Radius=2&Radius.unit=arcmin&submit=submit+id α Lac], a high proper motion star of 3.77 mag in V. |
|||
It was discussed and approved by the IAU WGSN in 2024. As this star is ..., the WGSN chose ... in the IAU-CSN. |
|||
== Weblinks == |
== Weblinks == |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[Category:Constellation]] |
[[Category:Constellation]] |
||
[[Category:Star Name]] |
|||
[[Category:Eurasia]] |
[[Category:Eurasia]] |
||
[[Category:European]] |
[[Category:European]] |
||
Latest revision as of 11:37, 25 September 2024
Hevelius, who invented the constellation Lacerta sive Stellio (modern Lacerta), gave it the alternative name Stellio in his star catalogue and atlas.
Etymology and History
Latin "Stellio", literally "star lizard", derives from "stella" (star). It designates a newt, an olive-green lizard with spotted back, typically found in the rocky areas around the Mediterranean. It is also known as "stellion" or "rock agama"; scientific name is Laudakia stellio of the family of the Agamidae.
In the introduction of their atlas, Jan and Elizabeta Hevelius claim that they have named this region after a lizard because the lizard is squeezed into such a narrow gap between existing constellations that no larger animal could fit there.[1]
On Hevelius’s chart (right) there is a triangle of stars above the head of Lacerta that are shown as part of the turban of Cepheus. These stars are now included in Lacerta, and are known as Alpha Lacertae (mag. 3.8), Beta Lacertae (4.4), and 9 Lacertae (4.6). The Greek letters were allocated by Francis Baily in his British Association Catalogue of 1845.
Mythology
It is not preserved why they applied an alternative name here, "Lacerta sive Stellio" (The Lizard or the Stellion), but it might be a pun as there are real animals called "star lizards" while they formed the image of a lizard out of stars.
IAU Working Group Star Names
Following the Almagest-tradition of using alternative names for the constellation given by its creator to the brightest star in the group, the name "Stellio" was suggested for the brightest star in Lacerta, α Lac (Alpha Lacertae). It was discussed and approved by the IAU WGSN in 2024.
On August 29th 2024, the IAU WGSN decided to adopt the name "Stellio" for α Lac, a high proper motion star of 3.77 mag in V.